How Does the Honda Pilot Tire Pressure System work?
The Honda Pilot tire pressure monitoring system, also known as TPMS, is a safety feature designed to warn drivers when the air pressure in any of the vehicle’s tires falls below a certain level. Here’s a detailed overview of how this system works:
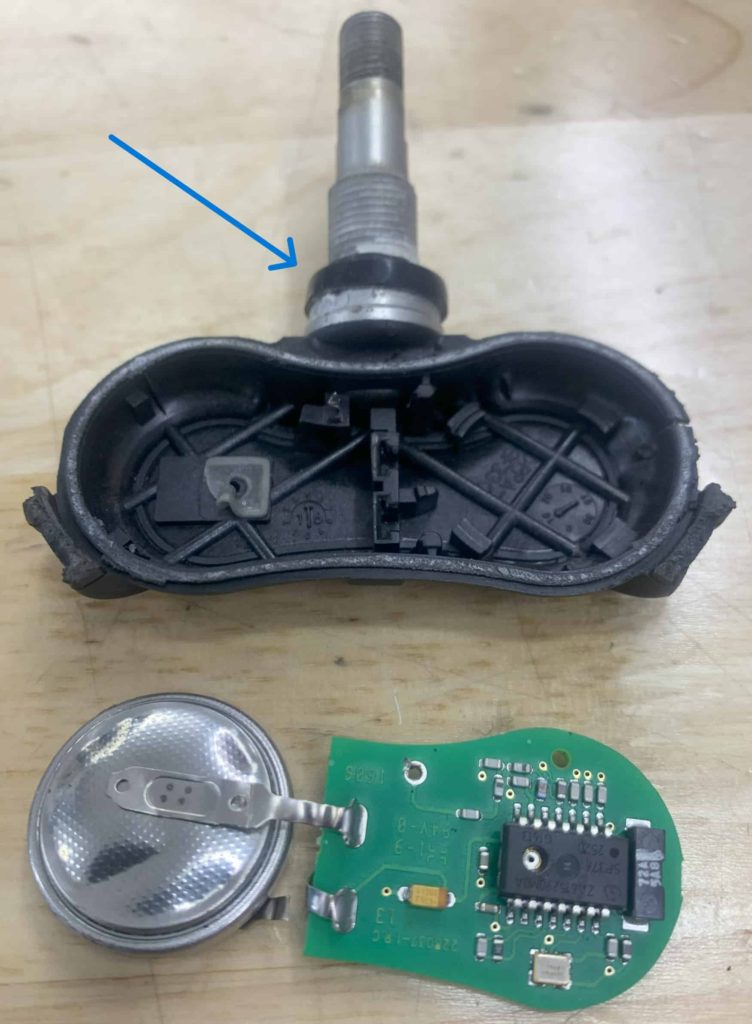
Sensors and Transmitters: Each tire on the Honda Pilot (including the spare on some models) has a sensor/transmitter attached to the valve stem inside the tire. These sensors are designed to monitor the air pressure within the tire continuously. They are battery-powered devices.
Data Transmission: These sensors communicate wirelessly with the vehicle’s onboard computer system. The sensors send information to the car’s computer about each tire’s air pressure levels. This is done via radio frequency signals.
Threshold Levels: The car’s computer system has pre-set tire pressure levels, which are considered safe by Honda for the Pilot model. These levels can vary depending on the vehicle’s model and year, but a common standard is 35 PSI (pounds per square inch).
Data Analysis: When the computer receives signals from the sensors, it compares the pressure level of each tire to the pre-set safe levels.
Warning Indicator: If the air pressure in any of the tires drops significantly below the set standard (usually 15-25% below the recommended level), the TPMS warning light on the vehicle’s dashboard will turn on and make an audible sound. This is a signal for the driver to check the tire pressures and inflate them if necessary.
Steps to Reset Honda Pilot TPMS
2018-2023 Honda Pilot TPMS Reset Procedure
Step 1: Check and Adjust the Pilot Tire Pressure. Make sure all 4 tires are at the correct pressure levels. (35 Psi or 32 Psi depending on wheel and tire size)
Step 2: Turn the ignition to the ON position (press engine start button twice without your foot on the brake) or have the Pilot engine running.
Step 3: Select the HOME button on the top left of the infotainment system.
Step 4: Select SETTINGS on the infotainment screen.
Step 5: Select VEHICLE on the infotainment screen.
Step 6: Select TPMS CALIBRATION.
Step 7: Select CALIBRATE. (the TPMS indicator on the dashboard will blink and then turn off)
Step 8: Drive the Honda Pilot for a few miles at speeds over 20 Mph to complete the calibration process.
2012-2017 Honda Pilot TPMS Reset Procedure
Step 1: Check and Adjust the Pilot Tire Pressure. Make sure all 4 tires are at the correct pressure levels. (35 Psi or 32 Psi depending on wheel and tire size)
Step 2: Use the UP or DOWN arrows on the steering wheel to scroll and select VEHICLE SETTINGS. (the middle button between the up and down arrows is select)
Step 3: Select TPMS CALIBRATION.
Step 4: Select CALIBRATE. (The TPMS indicator on the dashboard will blink and then turn off)
Step 5: Drive the Pilot for a few minutes at speeds over 20 Mph to finish the calibration process.
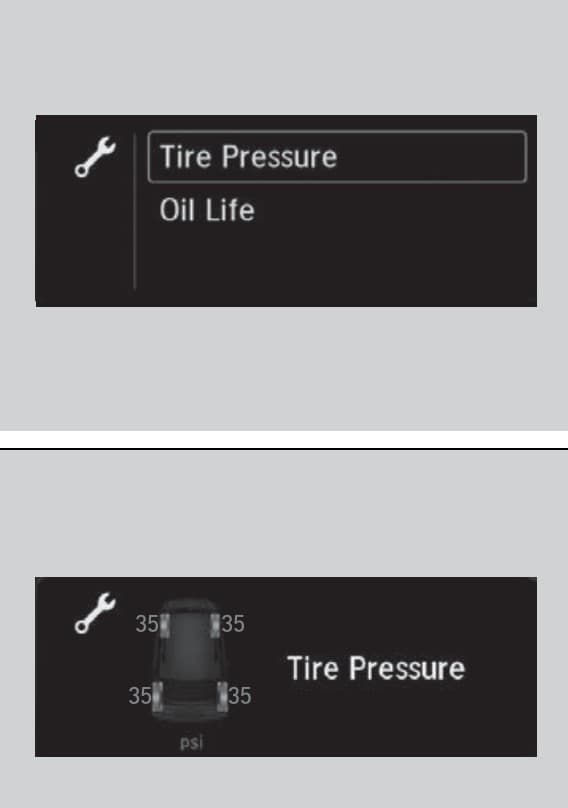
Steps to Access Honda Pilot Current Tire Pressure
Switch the Pilot ON.
Select the “HOME” button on the steering wheel.
Select the UP or DOWN arrows on the left side of the steering wheel until the “MAINTENANCE” option shows.
Select “ENTER” on the steering wheel and navigate to “Tire Pressure”
Select the “ENTER” button again. The current tire pressure details will display on the driver information interface.
When to Recalibrate Honda Pilot Tire Pressure System
After tire pressure has adjusted (inflated or deflated to correct the pressure).
After a TPMS sensor has been replaced or swapped.
After a tire rotation.
After tire balances or wheel alignments.
After any tire or wheel has been replaced. This includes swapping winter and summer tires.
After your Honda Pilot battery dies, is jumped, or charged.
Things to Know About Tire Pressure
Does the Weather Affect Tire Pressure?
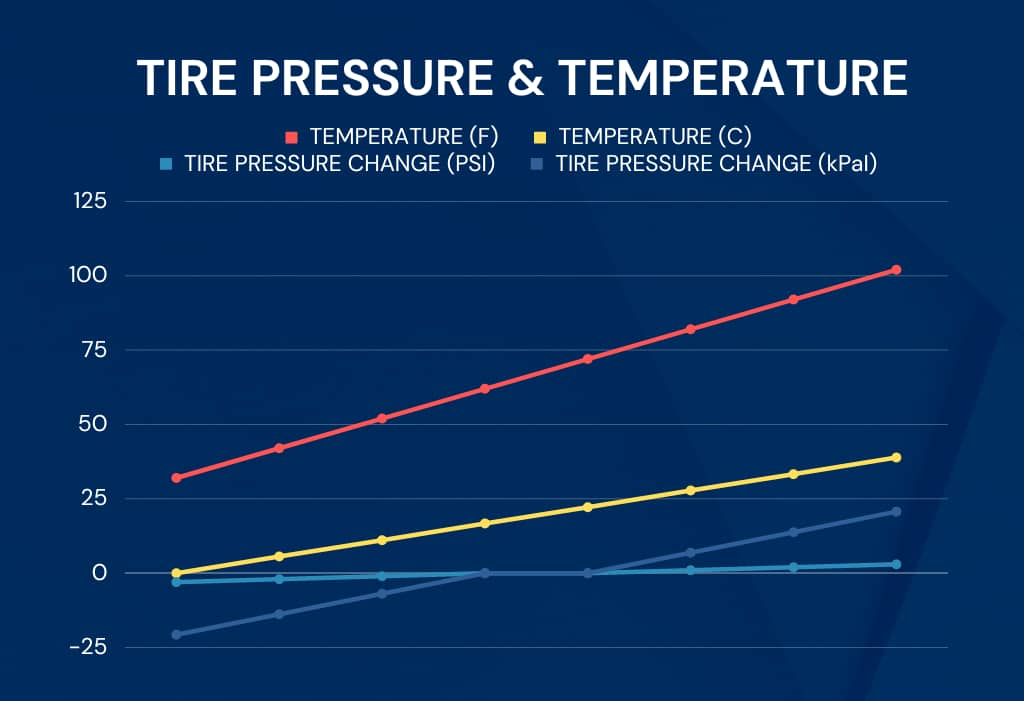
Weather plays a significant role in influencing tire pressure in your Honda Pilot. As a rule of thumb, for every 10 degrees Fahrenheit change in air temperature, your tire’s inflation pressure can change by about 1 PSI (pound per square inch). In colder weather tire pressure tends to decrease because the air inside the tire contracts which leads to a drop in pressure. In warmer weather the air inside the tire expands, causing an increase in tire pressure. This is why significant weather shifts can alter your tire pressure beyond the optimal range and set off the tire pressure indicator.
How to Check Tire Pressure
Gather Necessary Tools: Ensure you have a reliable tire pressure gauge. Many people prefer digital gauges for their accuracy and ease of reading.
Check Tire Temperature: Tires should be ‘cold’ when you check the pressure. Cold tires means the Pilot hasn’t been driven for at least three hours. This allows the tires to cool down and gives a more accurate pressure reading.
Locate the Valve Stem: On each tire you’ll find a valve stem sticking out from the rim. It’s typically covered with a small cap that you’ll need to unscrew and set aside (don’t lose it!).
Use the Pressure Gauge: Place the pressure gauge onto the valve stem and press down quickly and firmly. If you’re using a digital gauge the pressure will display on the screen.
Compare the Reading: Compare the readings on the gauge with the recommended tire pressure for your Honda Pilot.
Adjust Tire Pressure If Needed: If the tire pressure is too high let some air out and check the pressure again. If it’s too low add air at a service station or using a home air compressor until the correct pressure is reached.
Repeat for All Tires: Check all four tires and adjust as necessary. Don’t forget to check the spare tire as well.
Replace the Valve Caps: Once all tires are at the correct pressure replace all the valve caps. They keep dirt and moisture out of the valve stem which can cause leaks.
2023 Honda Pilot Tire Size & Pressure
TIRE SIZE | FRONT PSI | REAR PSI |
245/60R18 | 35 | 35 |
265/45R20 | 32 | 32 |
SPARE | 60 | 60 |
Impacts of Driving With Underinflated Tires
Driving your Honda Pilot with underinflated tires can lead to several adverse effects, including:
Decreased Fuel Efficiency: Underinflated tires create more resistance on the road which means your vehicle has to work harder to move, thus consuming more fuel. This can significantly decrease your fuel efficiency.
Poor Handling: Tires that are not properly inflated can negatively affect the vehicle’s handling and responsiveness. This can make the Pilot harder to control especially in emergency maneuvers.
Increased Tire Wear: Underinflated tires wear out more quickly, especially on the outer edges of the tread where the tire makes extra contact with the road. This can lead to premature tire replacement.
Overheating: Underinflation increases friction between the tire and the road, leading to excessive heat. This can cause tire failure, blowouts, or even a fire in extreme cases.
Longer Braking Distance: Low tire pressure can increase the braking distance of the vehicle, leading to potential accidents, especially in critical situations. This can also wear down your brake pads at a faster rate.
Reduced Load Capacity: Tires that are underinflated cannot support the vehicle’s load as effectively which can make the SUV unstable, especially when carrying heavy loads or multiple passengers.
Increased Risk of Tire Damage: Underinflated tires are more susceptible to damage from potholes, debris, and other road hazards. The rims of the wheels can also be damaged if the tire pressure is extremely low.
Common Reasons the Honda Pilot Tire Pressure Light Turns On
Spare Tire: If you’re driving your Honda Pilot with a spare tire, also known as a “donut,” the tire warning light will be activated. (this will also cause the tire indicator to flash)
Seasonal Weather temperature changes: A shift in air temperature can result in a reduction in tire pressure.
Tire puncture or leak: Nails, screws, or other sharp objects (road debris) on the road can puncture the tire’s tread causing an air leak.
Faulty TPMS sensor: Damaged or faulty tire pressure sensors can cause the tire pressure light to malfunction and give incorrect air pressure readings.
Tire damage: Hitting potholes or bumping into curbs can cause structural damage such as bulges and bubbles on the tire sidewall. These damages can cause an air pressure leak on the sidewall of the tire or cause a bead seal leak between the rim and tire.
Sensor battery life: Each TPMS sensor has limited battery power and will eventually run out of juice.
Recent tire rotation or replacement: After tires have been rotated or replaced, it is necessary to recalibrate the Honda Pilot tire pressure monitoring system to prevent tire location issues. (After a tire rotation the tire pressure monitoring system can still think the front tires are in the rear and vice versa.)
Valve stem issues: A damaged or leaking valve stem (metal or rubber) can result in tire pressure loss, activating the air pressure warning indicator.
Cracked Wheel: Cracked, broken or damaged wheels can cause air to leak.
Altitude changes: A change in altitude while driving can affect tire pressure causing low tire alerts.
Natural pressure loss: Tires that are ignored and sit for long periods of time develop dry-rot as well as lose pressure naturally over time.
TPMS Software Updates: Occasionally Honda may put out a TPMS software update.
Is it Safe to Drive the Honda Pilot with the Tire Warning Light On?
It’s essential to know why the tire warning light in your Honda Pilot has been triggered to know if it is actually safe to drive with the tire light on. Could there be a tire puncture causing deflation? If so, is the rate of air loss slow or fast? Is the tire in good physical condition but the pressure sensors are not functioning correctly? While there may be scenarios where driving with the tire light on doesn’t pose an immediate threat, it usually indicates a significant safety issue. Understanding the root cause is crucial in making a knowledgeable and safe decision about whether to continue driving your Pilot with the tire warning light illuminated.
What is the Honda Pilot TPMS Malfunction Indicator? (Light Blinking)
The Honda Pilot has a TPMS malfunction indicator to warn the driver when the tire pressure system isn’t working properly. The malfunction indicator uses the same indicator light as the low tire pressure alert (yellow exclamation point), but it has a different purpose. When the Honda Pilot TPMS has an issue, the warning light will flash for 60 seconds and then stay on. This sequence will keep happening every time you drive the SUV until the problem is fixed.
Things to Know About the Honda Pilot Tire Pressure Sensor Batteries
Each tire pressure sensor in a Honda Pilot operates autonomously, fueled by an integrated battery akin to those in key fobs or wristwatches. The batteries are encased in a plastic housing and are directly connected to the sensor’s circuit board. Consequently, when the battery is depleted or near exhaustion the entire sensor must be replaced. The longevity of the battery can be influenced by a variety of factors, including driving conditions, climate variations, and the frequency and extent of your driving. According to Honda these sensor batteries are typically designed to last between 7 to 10 years. From my own experience having replaced numerous TPMS sensors, I’ve seen batteries with a lifespan ranging from 3 or 4 years to as long as 20 years.
Troubleshooting the Honda Pilot Tire Pressure Warning Light
If you’re encountering problems with the tire pressure light on your Honda Pilot, here are several strategies you might consider to address these issues:
Option 1: Is a Tire Losing Air?
Should the tire pressure light turn off after inflating the tires, only to reappear a few minutes, hours, or days later, this is indicative of a leak in one of your tires. If the tires are retaining air and maintain the precise recommended pressures every time you check, then the issue lies elsewhere.
Option 2: Re-Activate a Dormant Tire Sensor
If your tire light is on but you’re confident that your tires aren’t losing air, sometimes the sensor needs to be “re-activated”. Identify the sensor that’s causing the problem, then reduce the pressure of the respective tire by about 15 to 20 Psi before reinflating it to the standard 35 Psi. Then add an extra 10 Psi, for a total of 45 Psi. Next, take your Honda Pilot for a short drive. For safety considerations steer clear of highways or congested roads. After about 10 to 15 minutes of driving, stop your vehicle. Then release the extra 10 Psi back to the recommended 35 Psi and take your car out for another drive.
Option 3: Erasing the Honda Pilot Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC)
If you’ve tried all other solutions and your tires don’t seem to be losing air, you can manually clear the error codes from your Honda Pilot’s electronic control unit (ECU) by disconnecting the negative terminal of your vehicle’s 12-volt battery. Keep it disconnected for several minutes before reconnecting the terminal. This action effectively wipes out all existing fault codes from the ECU, including the one causing the tire pressure warning light to illuminate. If the tire light switches off but reactivates after carrying out this process, it’s probable that a sensor is faulty or there’s an actual leak in your tire.
Option 4: Check the Battery Status of Each Tire Pressure Sensor
To execute this diagnostic process, a TPMS programming or relearning tool is necessary. Despite each TPMS tool having its own unique set of functions, the procedure is generally similar. You’ll need to scan each pressure sensor by positioning the TPMS tool close to the tire valve stem and selecting a “test” function. Once all four pressure sensors have been assessed, the tool will provide a status report for each, including information about their residual battery life. If the battery status is indicated as “low”, it implies that the corresponding sensor requires replacement.
Option 5: Does the Tire Light Come On and Then Turn Off?
If the tire light comes on when you first start your Honda Pilot but then switches off as you drive, it’s probable that your tire pressure is slightly lower than the recommended levels. This can happen because your tires start the day cold (for example at 31 Psi), and as you drive the tires heat up which increases the pressure (for example to 35 Psi), subsequently deactivating the low tire warning light. The solution for this issue is to make sure each tire is inflated precisely to 35 Psi.
Tire Leaks and Solutions
How to Find a Tire Leak
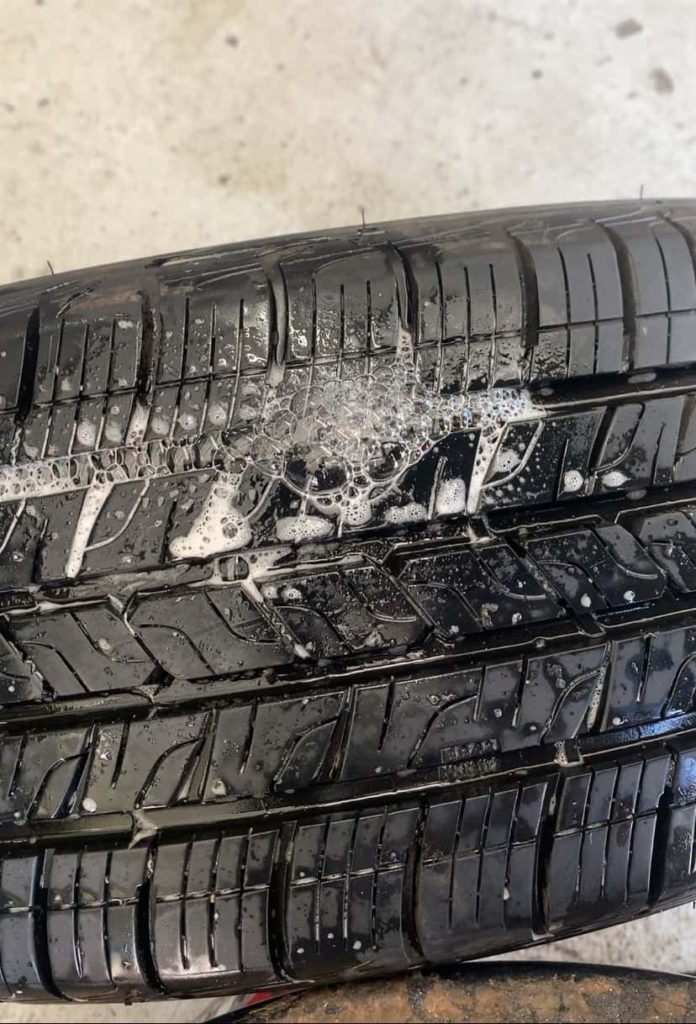
To find a tire leak in your Honda Pilot, begin by checking the air pressure in all four tires to pinpoint the one that’s underinflated. Inflate that tire to a minimum of 35 Psi, since detecting a leak in a completely deflated tire can be tricky. Next, prepare a soapy water mix (by mixing soap and water) in a spray bottle, or opt for a ready-made solution like Windex. Generously spray this mixture all over the tire (don’t forget to spray the valve stem and bead seal) ensuring the whole tire is doused. Be on the lookout for tiny bubbles surfacing on the tire. If there’s a leak, the air escaping will form small bubbles at the leak source. Bear in mind: If the tire is losing air, a leak is somewhere to be found, so keep spraying and searching!
Are Tire Plugs Safe?
The straightforward response is a resounding YES! Having serviced hundreds of tires with plugs in auto repair centers, I can vouch for their effectiveness and dependability. Tire plugs are particularly good at repairing punctures in the tire tread, as they form a seal that prevents air leaks. Tire plugs are constructed from sturdy, rubber-like materials that can endure drastic changes in the tire’s internal air pressure and temperature. When properly applied a tire plug can last for the rest of the tire’s lifespan. It’s crucial to remember that tire plugs are not intended to fix damage to the tire’s sidewall.
Are Tire Sealants Safe?
The application of tire sealants (also known as Fix-a-Flat) should ideally be limited to emergency scenarios. When you introduce a tire sealant into the tire valve stem, you’re effectively injecting a liquid into the tire. This could potentially harm the tire pressure sensor electronics and interfere with the tire’s balance (causing vibrations). If you find yourself in a situation where a tire sealant is necessary, we recommend driving your Honda Pilot directly to a tire service station or Honda dealer and let them know that you’ve used a tire sealant.
Emergency Tire Tools to Keep in the Car
There are a number of tools we recommend keeping in your Honda Pilot for emergency tire situations. These include:
Impact wrench to loosen lug nuts
19mm, 21mm or 22mm socket for lug nuts
Tire plugs and tire plug kit
Tire sealant / Fix a Flat
Tire pressure gauge
Are Tire Pressure Sensors Legally Required in the Honda Pilot?
In many regions including the United States and Europe, legislation mandates the installation of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems in vehicles. According to the TREAD Act enacted in the U.S. in 2000, all vehicles manufactured post-September 2007 are required to include a TPMS. The law primarily targets vehicle manufacturers, aiming to enhance road safety by notifying drivers of substantial changes in tire pressure. Likewise, as of November 2012, European regulations stipulate that all new passenger vehicles must have a TPMS installed. These regulations aim to decrease the frequency of accidents resulting from tire-related problems.
Everything in this article is applicable to all 2024 Honda Pilot models and trims including the Honda Pilot LX, Sport, EX-L, TrailSport, Touring, and Elite.
Please note that this blog post contains Amazon affiliate links. This means that if you make a purchase through one of these links, we at TPMSRESET.COM may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products that we personally use and believe in. Thank you for supporting us.