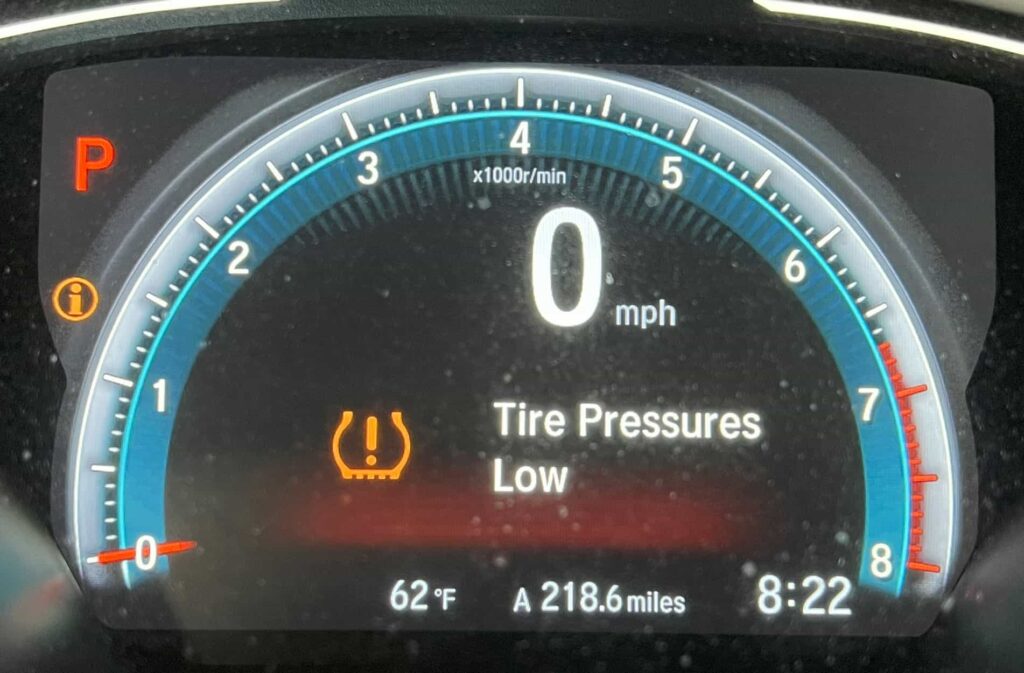
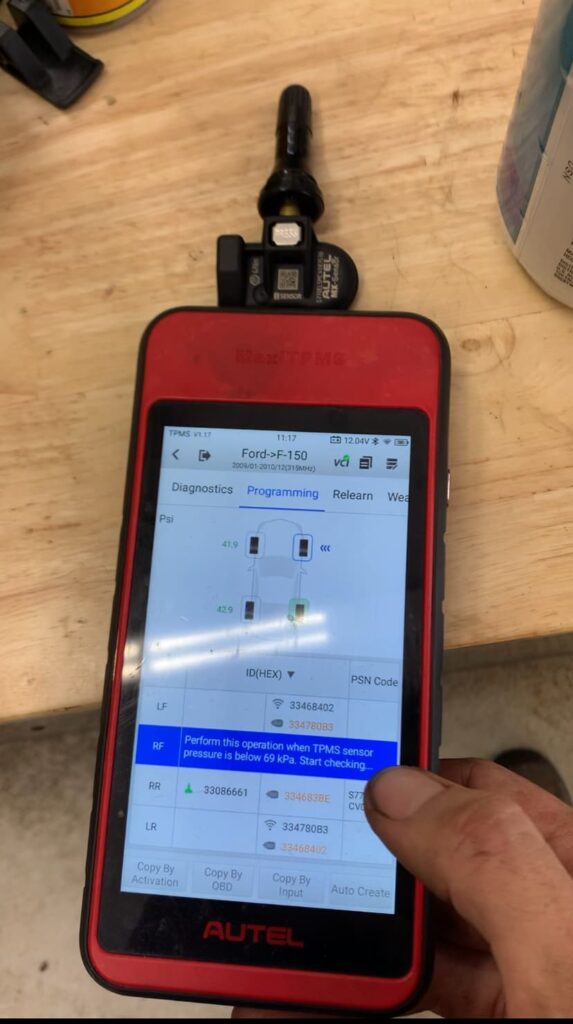
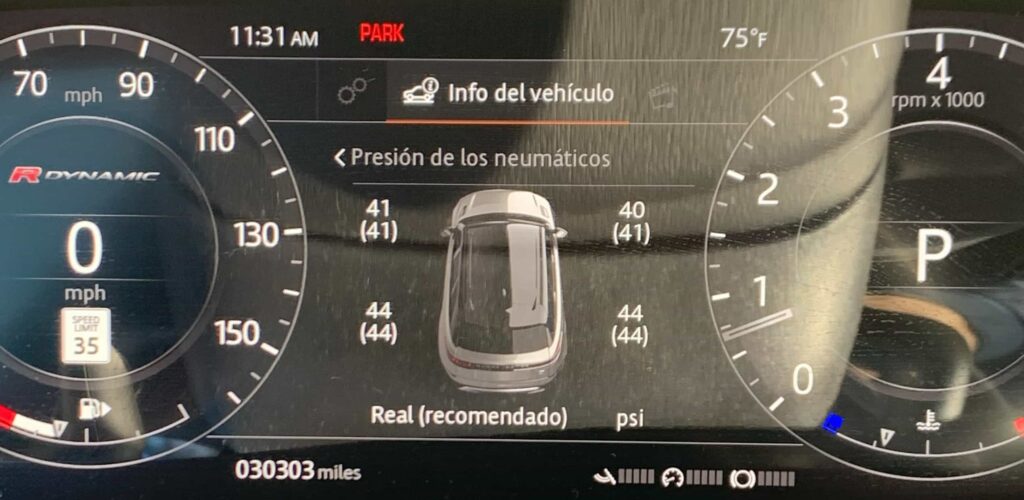
If your tire pressure light is on, keep reading. We all know how frustrating a low tire pressure light on the dashboard is so understanding why it’s on and how it works is essential. The importance of maintaining proper tire inflation cannot be overstated, as it’s integral not only to the longevity of your tires but also to the overall safety and efficiency of your vehicle. Underinflated tires can lead to a myriad of issues, including increased fuel consumption, uneven tire wear, and in severe cases, dangerous blowouts. Fortunately, the innovation of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS), especially through the utilization of tire pressure sensors, offers a formidable solution. These sensors, which are crucial components of direct TPMS, vigilantly monitor the air pressure within your tires, providing timely alerts when deviations from the recommended levels occur. This article will guide you through the realm of tire pressure sensors in 2024, explaining their functionality, the significant advantages they bring to vehicle upkeep, and the essential maintenance practices necessary to ensure their optimal performance.
Understanding Tire Pressure Sensors
Tire pressure sensors are at the heart of every direct Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS). Their primary function is to monitor the air pressure inside the pneumatic tires of vehicles and alert drivers through a warning light or message on the dashboard when the air pressure falls below or rises above recommended levels. As we explore the world of tire pressure monitoring systems and tire pressure sensors in 2024, it’s crucial to understand their types, how they work, and the undeniable benefits they bring to vehicle safety and performance.
Types of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
There are two main types of tire pressure monitoring systems: Direct TPMS and Indirect TPMS. Each has its unique method of monitoring tire air pressure, catering to different vehicle needs and manufacturer preferences.
Direct TPMS: This system uses sensors that are located in the tire and directly measure the pressure in each tire, sending real-time data to the vehicle’s computer system (ECU) using wireless technology. Direct TPMS provides accurate readings and can alert the driver to which specific tire is experiencing issues. This electronic system is known for its specificity and accuracy.
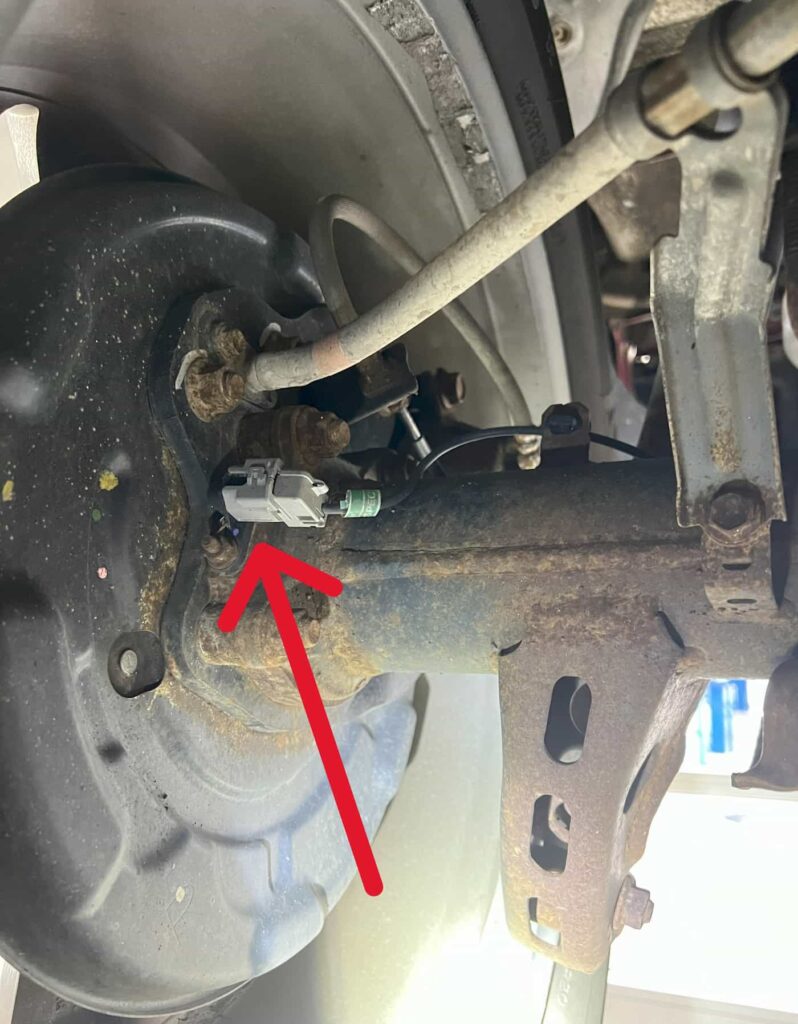
Indirect TPMS: Instead of measuring the tire pressure directly using sensors, indirect TPMS systems use the vehicle’s wheel speed sensors to monitor the speed of each wheel. A tire with lower pressure will rotate at a different speed than the others, which is detected by vehicles on board computer. While less expensive than direct TPMS, indirect systems can occasionally display inaccurate readings and may not alert the driver to gradual pressure decreases unless the vehicle is moving.
How Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems Work
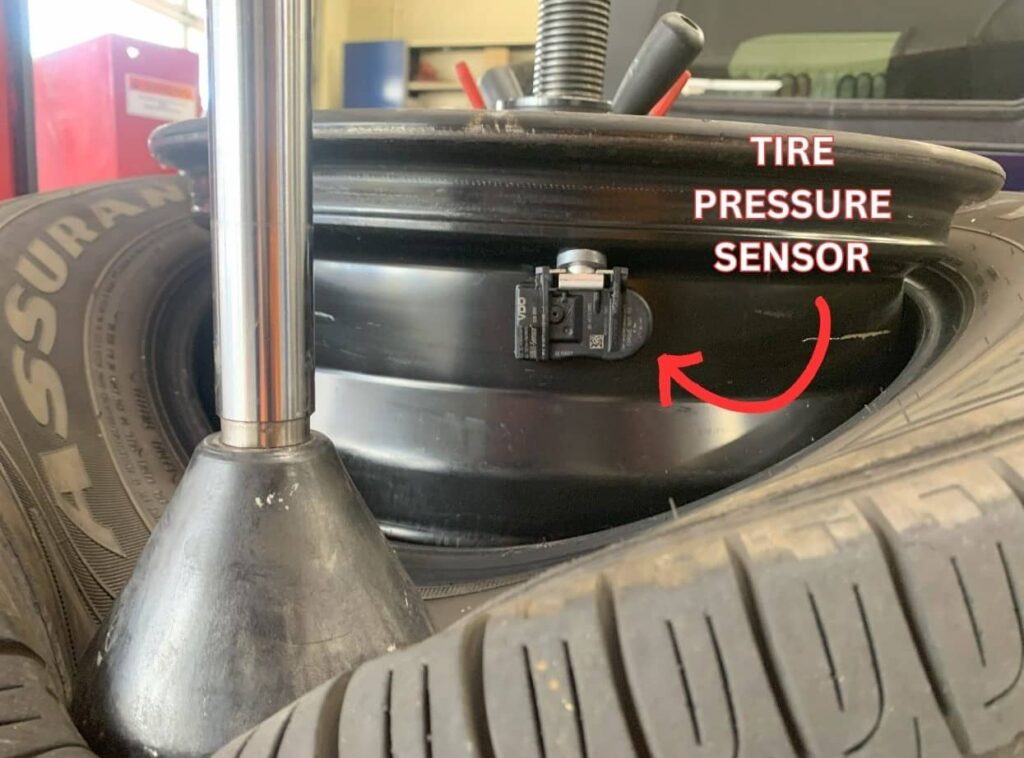
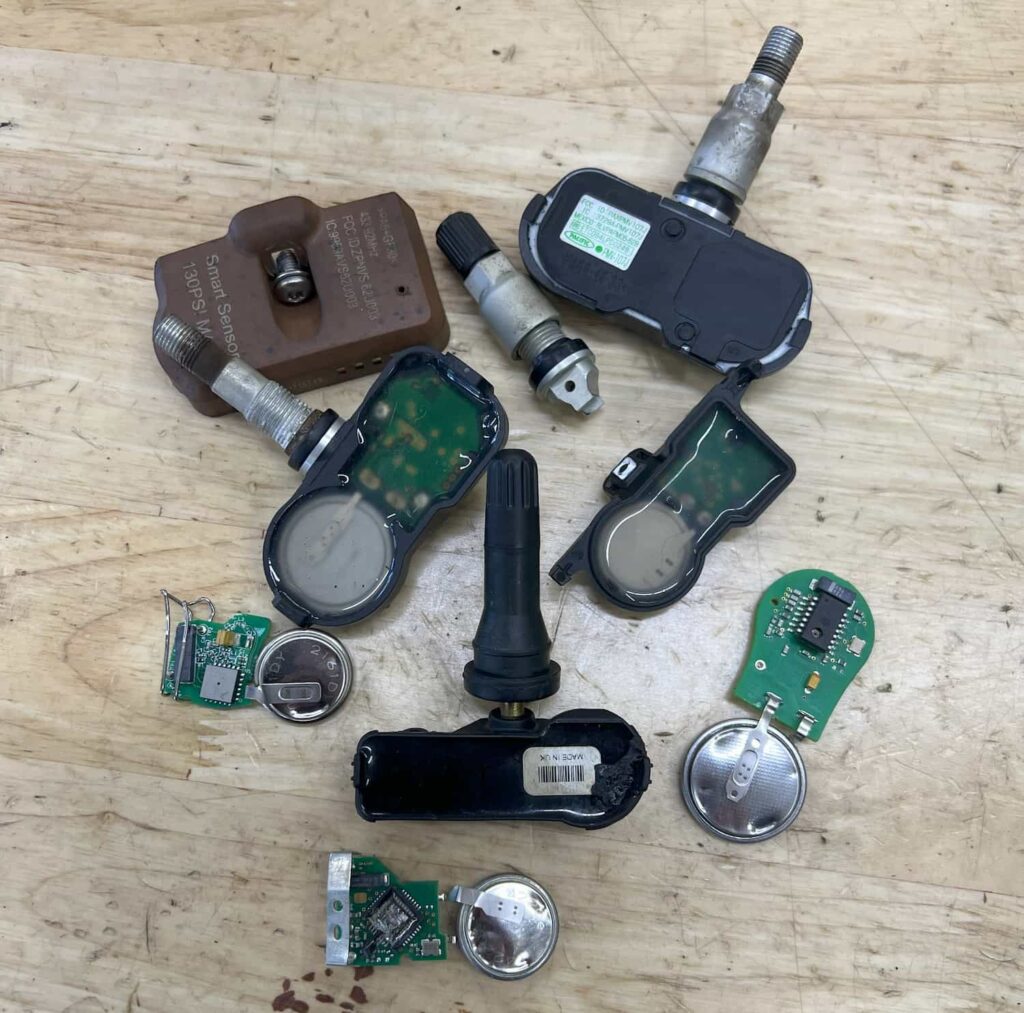
Direct TPMS consist of air pressure sensors in tires, a TPMS receiver module, and the vehicle’s ECU. Each tire pressure in the system is encased in a small plastic housing attached to the valve stem, comprising several key components: a microcontroller, a battery, a pressure transducer, and a transmitter with an integrated antenna. The pressure transducer’s role is to convert the physical tire pressure into an electrical signal, which the microcontroller then processes into interpretable data. This data is wirelessly transmitted to the vehicle’s Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) receiver module via the transmitter and antenna, using a specific radio frequency for communication (typically 315 mHz or 433 mHz).
The TPMS receiver module, crucial for the system’s functionality, is strategically positioned inside the vehicle, often beneath the dashboard or close to the center console. It continuously collects air pressure data from each tire’s sensors while the vehicle is in motion, decoding and associating the received signals with the respective tires. This processed information is relayed to the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU), which evaluates the tire pressure against the manufacturer’s predefined standards. Any significant discrepancy prompts the ECU to trigger an alert, displayed on the dashboard through a yellow exclamation point, a message, or real-time pressure readings on the information display.Indirect TPMS systems calculate tire pressure indirectly through wheel speed sensors that are part of the anti lock brake system and traction control systems. By analyzing the rotational speed of each wheel, the system can infer pressure variations and signal when a tire is significantly under-inflated. The general principle is that an under inflated tire will have a reduced diameter, causing the tire to spin faster than the others.
Benefits of Tire Pressure Monitoring
Monitoring tire pressure is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity for maintaining vehicle efficiency, safety, and the longevity of your tires.
Safety: Properly inflated tires maintain optimal contact with the road, reducing the risk of tire failures like blowouts, especially at high speeds.
Fuel Efficiency: Tires at the correct pressure level offer less rolling resistance (friction between tire and road), improving fuel economy.
Tire Longevity: Even tire wear is ensured by maintaining proper tire pressure (and alignment), extending the life of your tires and saving you money in the long run.
The ability of the tire pressure monitoring system to provide real-time data and warnings not only enhances the driving experience but also significantly contributes to road safety.
Installation and Maintenance of Tire Pressure Sensors
Proper installation and maintenance of tire pressure sensors are crucial for their accurate operation and longevity. Whether you are considering a DIY installation or seeking professional help, understanding the basics can help ensure that your TPMS functions effectively and you know what you’re talking about with your local mechanic.
Installing Tire Pressure Sensors
DIY Installation: For those who prefer the hands-on approach, installing direct TPMS sensors can be straightforward but requires some technical know-how and a tire machine. The process involves removing the tire from the wheel, attaching the sensor to the valve stem, and then reseating the tire to the wheel. Indirect TPMS systems, however, do not require manual installation of sensors in the tires as they utilize the vehicle’s existing wheel speed sensors.
Professional Installation: For most drivers, professional installation is recommended, especially for direct systems. Automotive repair and tire shops have the specialized equipment and expertise to install tire sensors properly, ensuring they are correctly calibrated and programmed with your vehicle’s onboard computer system by using a special TPMS tool.
Troubleshooting Common Direct TPMS Issues
Warning Light Activation: If your TPMS warning light activates, first check to ensure all tires are inflated according to the manufacturer’s specifications (Check the driver side door panel air pressure label). If the TPMS light remains on despite correct air pressure, one or more sensors may be malfunctioning or require recalibration.
Sensor Failure: Failure can occur due to battery depletion, damage, or loss of communication with the vehicle’s computer. If a sensor is not functioning, TPMS diagnostic tools can help identify the issue, which usually results in sensor replacement.
Interference: Occasionally, electronic interference from other devices or extreme window tints can affect sensor performance. Ensure that any aftermarket electronic devices installed in your vehicle are not interfering with the TPMS system.
Troubleshooting Indirect TPMS Issues
Besides driving with low tire pressure, a very common cause for indirect TPMS low tire pressure light to be triggered is when one or more tires is a different brand, model, or size to be different from the others. The slightest discrepancy in tire sizes will set off the low tire pressure warning light. If a wheel speed sensor is damaged or not working properly as well as driving with an uneven load (or too much load) in your vehicle will also set off the light. Another common cause is when driving with extreme tread or wheel damage.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance for Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) are subject to various regulatory standards worldwide. Understanding these regulations is essential for vehicle manufacturers, owners, and operators to ensure compliance.
Global Standards for Tire Pressure Monitoring
Different countries and regions have established their own standards and requirements for TPMS:
In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) requires that all vehicles produced after September 2007 be fitted with a Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) to warn drivers about substantial low tire pressure in any of the four tires. The regulation, known as the TREAD Act, was implemented to enhance road safety and reduce accidents caused by tire failures.
European Union: Regulation (EC) No 661/2009 requires that all new passenger car models built from November 2012 onwards must be fitted with a tire pressure monitoring system. This regulation aims to improve road safety and reduce CO2 emissions.
Other Regions: In countries such as South Korea, Russia, and Japan, regulations mandating TPMS have been implemented to promote vehicle maintenance and prevent tire failure through proper tire maintenance.
Compliance for Manufacturers and Vehicle Owners
Manufacturers: To comply with these regulations, vehicle manufacturers must ensure that all new vehicles are equipped with TPMS that meet or exceed the regulatory standards of their respective markets. This includes ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and durability of the sensors and systems installed.
Vehicle Owners: Compliance for vehicle owners primarily involves maintaining the TPMS in proper working condition. This includes checking the tire’s pressure, sensor battery checks, and ensuring that the system is functional at all times. In some jurisdictions, vehicle inspection programs include TPMS functionality checks, and failure to meet these standards can result in state inspection failure.
Side Note: I am personally a licensed state inspector in New Jersey and TPMS checks are not a part of the inspection process.
The Future of Tire Pressure Monitoring Regulations
The future of tire pressure monitoring regulations is likely to see stricter safety standards, driven by a relentless pursuit of enhanced vehicle safety. As technology advances, we can expect TPMS to become more sophisticated, offering greater accuracy and the ability to monitor additional parameters, such as tire temperature and tire wear. This evolution will likely lead to regulations mandating these advanced features in all new vehicles.
Integration with other vehicle safety systems, such as electronic stability control and automated emergency braking, is another anticipated trend. This integration could create a more comprehensive regulatory framework that addresses multiple safety aspects. Additionally, the scope of TPMS regulations may broaden to include more vehicle types, including heavy-duty trucks and buses, to bolster road safety across a wider range of vehicles.
Environmental concerns and fuel efficiency are also expected to influence future TPMS regulations. As vehicles become more connected, TPMS could be part of a networked system providing real-time data and predictive maintenance, helping to ensure tires are always properly inflated. This not only enhances safety but also contributes to better fuel economy and reduced emissions, aligning with global environmental goals.
Choosing the Right Tire Pressure Sensor
If you have to replace a TPMS sensor (only if your vehicle uses direct TPMS), choosing the right one for your vehicle is more than just a technical necessity; it’s a decision that affects your vehicle’s safety, efficiency, and tire longevity (It can also prevent lots of headaches). With the market offering a plethora of options, understanding what to look for in a tire pressure sensor is essential.
Factors to Consider When Buying
Compatibility: Ensure the sensor is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Compatibility is crucial for the sensor to properly communicate with the vehicle’s onboard computer system.
Battery Life: Since the battery in most direct TPMS sensors cannot be recharged or replaced, selecting a sensor with a long battery life (usually 5 to 10 years) is important to avoid frequent replacements.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Consider sensors that are easy to install and do not require constant recalibration or programming.
Price: Although price shouldn’t be the only consideration, selecting a sensor that provides excellent value is crucial.
Top Brands and Models
Several manufacturers are recognized for producing high-quality tire pressure sensors. Each brand offers various models designed to suit different vehicle types and requirements. For instance:
Schrader: Known for its pioneering role in TPMS technology, Schrader sensors are widely used by OEMs and are renowned for their durability and reliability.
Autel: These TPMS sensors are after-market and are suitable to replace any OEM tire pressure sensors as long as you have an Autel TPMS programming tool.
Bosch: Bosch sensors are designed for easy installation and compatibility with a broad range of vehicles, ensuring high performance and reliability.
Recommendations
Our recommendation is to always replace a TPMS sensor with either the OEM sensor or a universal sensor such as the Autel tire pressure sensors.
FAQ
How Much Does it Cost to Replace a Tire Pressure Sensor?
Tire pressure sensors can cost between 25$ to 100$ per sensor. Tire pressure sensor replacement and installation on most vehicles can cost between 40$ and 75$.
How Do I Know If MY Vehicle Has Direct TPMS or Indirect TPMS
An easy way to identify if your vehicle uses a sensor system is by checking the valve stems. If the valve stems are metal, your vehicle has sensors.
Can You Drive With a Bad Tire Sensor and How Far Can You Go?
Driving with a bad tire pressure sensor is not technically unsafe unless the tire air pressure is low but the low tire pressure indicator light will stay on until the issue is resolved.
There is not a set distance you can safely travel when the tire light is on. The most important thing is to check if any tire is under inflated or over inflated.
What Happens When a Tire Sensor Goes Bad?
The tire pressure warning indicator will flash and then remain illuminated until the sensor is replaced.
How Do I Reset My TPMS?
A tire pressure monitoring system reset procedure varies depending on the vehicle make. Some vehicles have a TPMS reset button, some are calibrated through the dashboard information display, and some need to be driven at speeds over 25 Mph for at least 10 minutes.
Are TPMS Sensors in the Wheel or Tire?
Tire pressure sensors are mounted inside the tire on the wheel at the base of each valve stem.
What Does it Mean When the TPMS Light Comes On?
If the TPMS light turns on it means your vehicle either has low tire pressure or one or more sensors are low on battery power.
Why is My TPMS Light on But Tires Are Fine?
If the TPMS light remains illuminated even when the tires don’t have low pressure, either your tire pressure monitoring system needs to be reset or a sensor likely needs to be replaced. Use a TPMS diagnostic tool to determine which sensor is low on battery power.
What Do I Do if the TPMS Light Comes On?
Pull over and manually check the tire air pressure with a digital tire pressure gauge.
About the Author
STEFAN A.
Professional Automotive Technician – I am currently an automotive technician in New Jersey and have worked in private shops as well as dealerships. When I am not writing articles I am wrenching on race cars and driving radio controlled cars at the track!
Please note that this blog post contains Amazon affiliate links. This means that if you make a purchase through one of these links, we at TPMSRESET.COM may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products that we personally use and believe in. Thank you for supporting us.