In the modern vehicle’s arsenal of safety features, the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) stands out as a critical component, dedicated to ensuring your tires are always at their optimal pressure. Central to this system are the tire sensors, which continuously monitor the pressure levels and alert you the moment any discrepancies arise.
However, like any technological tool, these sensors are not immune to failure. But how can you tell which tire sensor is bad? Identifying a malfunctioning tire sensor is paramount to maintaining your vehicle’s health and, more importantly, your safety on the road.
The repercussions of a faulty tire sensor extend beyond just an illuminated dashboard warning light. It can lead to inaccurate tire pressure readings, compromising your vehicle’s handling, fuel efficiency, and the overall integrity of your tires.
By equipping yourself with the knowledge to tackle tire sensor troubles, you not only enhance your vehicle’s performance but also contribute to the safety of every road user.
Understanding Tire Sensors and Their Role
Tire pressure sensors are the unsung heroes of your vehicle’s safety system, diligently working behind the scenes to ensure your tires are properly inflated. These small yet powerful devices play a critical role in maintaining optimal tire pressure, which is essential for safe driving conditions.
Types of TPMS
If your vehicle has a tire pressure light, it either uses a direct tire pressure system or an indirect tire pressure system.
Direct TPMS
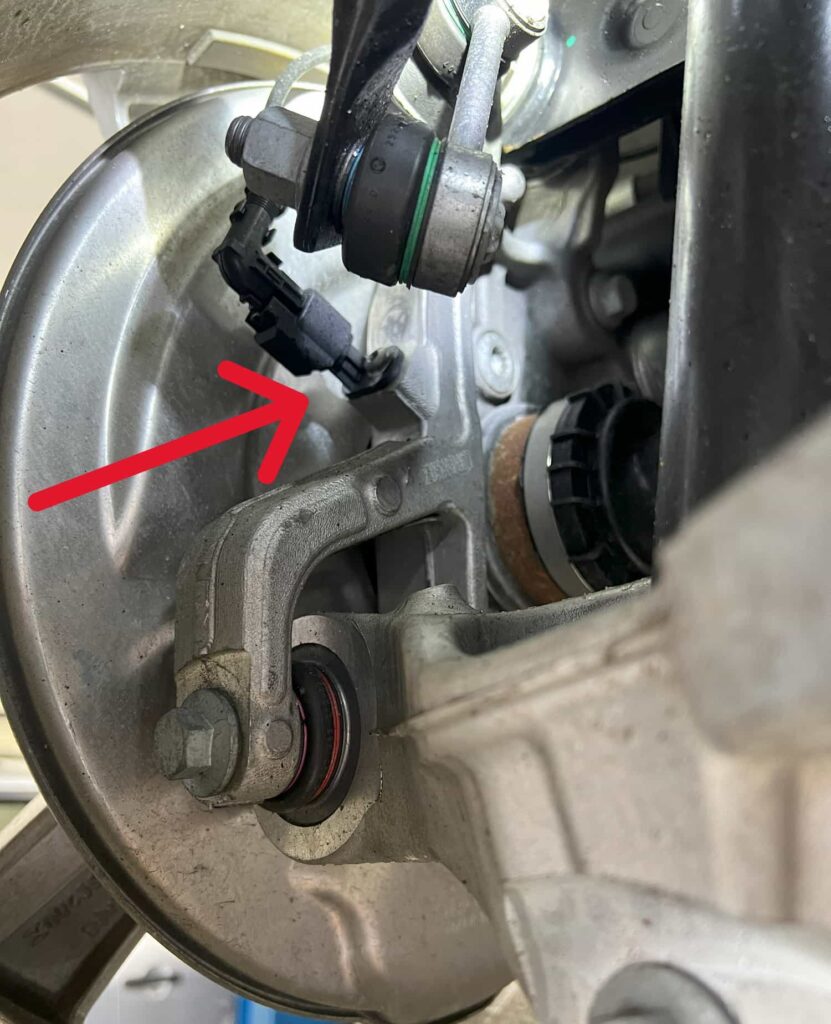
Direct TPMS uses a tire pressure sensor located in each tire, directly measuring the air pressure inside. These sensors send real-time data to the vehicle’s computer system, providing accurate readings of each tire’s pressure. This type of sensor is known for its precision and reliability.
Indirect TPMS
Unlike their direct counterparts, indirect TPMS systems do not measure tire pressure directly. Instead, they monitor the rotational speeds of the tires using data from the wheel speed sensors, using this information to infer pressure levels. This method is based on the principle that an under-inflated tire will rotate at a different speed compared to well-inflated ones.
Note: Every time we use the words TPMS sensor or tire pressure sensor, we are talking about a direct tire pressure system.
Functionality of Tire Sensors
Each tire pressure sensor is pivotal in preempting potential tire-related hazard by providing early warnings to the driver via a dashboard TPMS light. An adequately functioning TPMS sensor ensures:
Optimal Tire Pressure: Maintaining the correct tire air pressure is essential for maximizing fuel efficiency, reducing tire wear, and ensuring the vehicle handles as designed.
Safety: Correct tire pressure is crucial for the safety of the vehicle’s occupants. It ensures that tires have the best possible grip on the road, especially in adverse conditions.
Efficiency: Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, which in turn improves fuel economy.
Common Symptoms of a Bad TPMS Sensor
Warning Signs on Your Dashboard
TPMS Warning Light
One of the most straightforward indicators of a potential issue with a TPMS sensor is the low tire pressure warning light on your dashboard. This symbol, often resembling a tire with an exclamation mark, can illuminate for several reasons, including a significant change in tire pressure or a failure in the tire pressure monitoring system itself. While sometimes it might just indicate low tire pressure, flashing or persistent illumination could point towards a malfunctioning sensor.
Other Dashboard Signals
In addition to the TPMS warning light, other indicators on your dashboard might hint at a tire sensor problem. Because indirect tire pressure systems use the wheel speed sensors to measure air pressure, if a wheel speed sensor stops working, this will also cause the ABS and traction control lights to illuminate on the dash. Unusual messages or symbols related to tire pressure or vehicle stability control systems can also be triggered by sensor issues.
Physical Symptoms and Performance Issues
Unusual Tire Wear Patterns
Faulty or bad TPMS sensors can lead to incorrect tire pressure readings, causing drivers to unknowingly drive on underinflated or overinflated tires. This can result in uneven or accelerated tire wear, which not only shortens the lifespan of your tires but can also compromise your vehicle’s grip and safety on the road.
Changes in Vehicle Handling and Fuel Efficiency/Battery Range
Improper tire pressure, undetected due to a faulty TPMS sensor, can significantly affect your vehicle’s handling. You might notice that your car pulls to one side or that the steering feels unusually heavy or light. Additionally, incorrect tire pressure can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and EV Range, as the engine or electric motor works harder to move the vehicle forward.
Diagnosing Which Tire Sensor is Faulty
Determining which tire sensor is not functioning correctly is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s safety and performance. Here are effective strategies to identify the faulty sensor.
Manual Inspection and Troubleshooting Steps
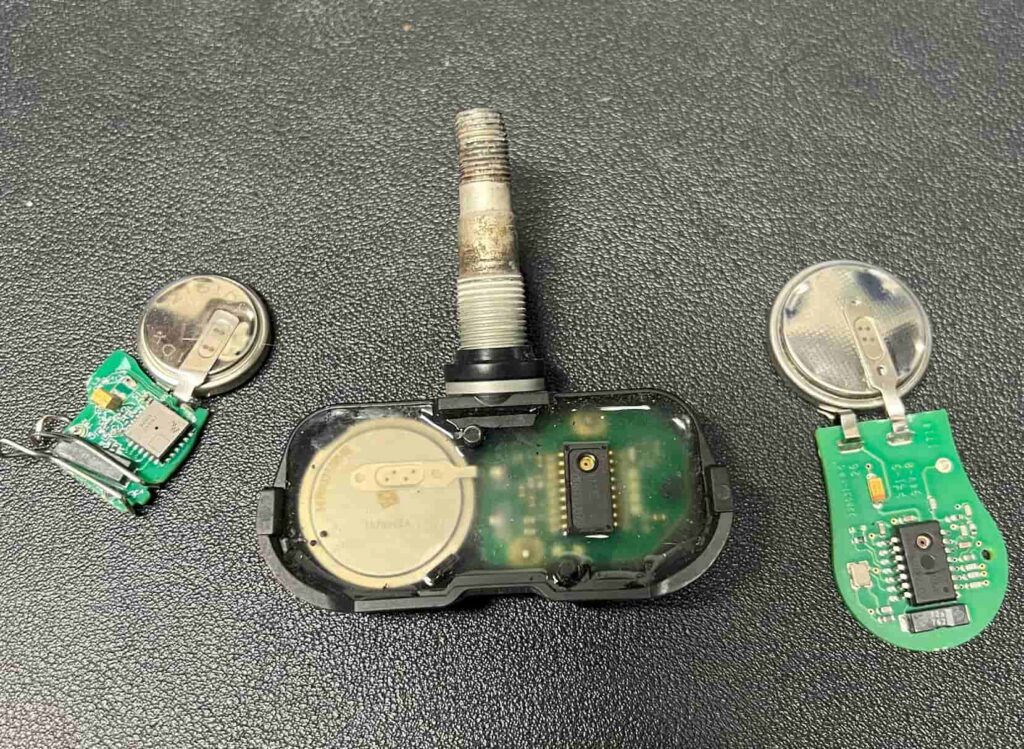
Visual Inspection for Physical Damage
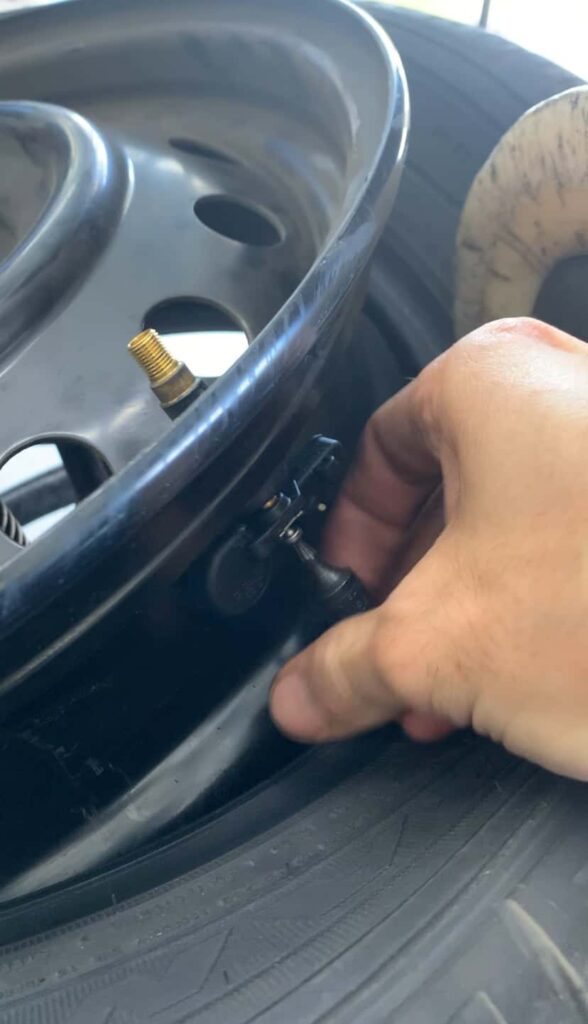
Start with a thorough visual inspection of each tire sensor, if accessible. Look for obvious signs of damage, such as cracks, loose components, or corrosion. Make sure the valve stem core (inside the valve stem) is tight and not leaking air. Also, make sure the 11mm nut on the metal valve stems is tight. Physical damage to a sensor is a clear indicator that it needs replacement.
Checking Tire Pressure With a Manual Gauge
Using a reliable manual tire pressure gauge, check the pressure in each tire, comparing the readings with the recommended pressure levels for your vehicle. Discrepancies between your manual readings and the vehicle’s TPMS readings could point to a faulty sensor. We recommend using a digital tire pressure gauge.
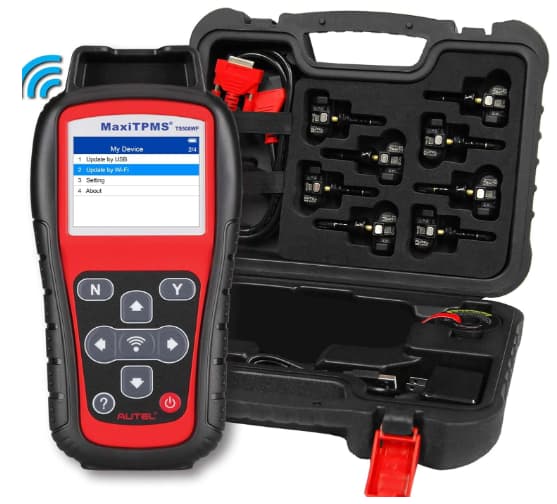
Using TPMS Diagnostic Tools
A TPMS scan tool will only work if your car or vehicle has a direct TPMS, meaning it has TPMS sensors.
How To Use a TPMS Diagnostic Tool
A TPMS diagnostic tool can communicate directly with each tire pressure sensor, providing detailed information about its condition and functionality. By scanning each sensor, the tool can identify which one is not responding or providing incorrect data.
Interpreting the Readings From a Diagnostic Tool
Diagnostic tools often display specific error codes when they detect a problem with a TPMS sensor. These codes can indicate a range of issues, from a tire sensor with dead batteries to a failure in transmitting data.
Analyzing Sensor Health Reports
Some advanced diagnostic tools provide detailed health reports for each sensor, including battery life, signal strength, and recent performance history. A sensor with a weak signal or low battery may not immediately require replacement but could signal that it’s nearing the end of its life. Borderline health sensors will still cause the low tire pressure light to illuminate on the car display panel.
Signal Strength and Responsiveness
The TPMS tool might also measure and report on the signal strength and responsiveness of each sensor. Sensors that consistently show weak signal strength or delayed responsiveness are likely candidates for replacement, as these issues can lead to inaccurate tire pressure readings and a TPMS light.
Cross Referencing With Vehicle Symptoms
Interpreting diagnostic readings becomes even more effective when combined with other symptoms your vehicle may be exhibiting. For example, if your vehicle’s TPMS warning light is on and the diagnostic tool identifies a sensor with a low battery, it’s likely that this sensor is the root cause of the warning light and needs to be replaced.
Replacing a Faulty Tire Sensor
When a TPMS sensor fails, replacing it promptly is vital to maintain your vehicle’s safety and operational efficiency.
When to Seek Professional Diagnosis and Replacement
Professional technicians have the expertise and tools necessary to diagnose and replace bad tire pressure sensors accurately. They can also recalibrate and program the TPMS system to ensure it’s functioning correctly with the new TPMS sensor.
DIY TPMS Replacement Tips
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Tire Sensor
For those comfortable with vehicle maintenance tasks, replacing a tire sensor can be a manageable DIY project. Here’s a simplified overview:
Wheel Removal: Loosen the lug nuts (while the vehicle is still on the ground), then lift the vehicle with a jack and remove the wheel.
Sensor Removal: With the tire completely deflated, break the bead seal between the tire and rim. Locate the tire sensor, typically mounted on the inner side of the wheel, and carefully remove it. This usually involves loosening a torx screw on the bottom of the valve stem and then pulling the bad TPMS sensor out.
Install the New Sensor: Position the new sensor correctly and secure it in place by pulling it through the valve stem hole in the wheel.
Wheel Reinstallation: Inflate the tire (make sure the tire bead seals on the rim) and put the wheel back on the vehicle.
TPMS Reset/Relearn: Follow your TPMS programming tools instructions and your vehicle’s procedure to reset or relearn the TPMS system, ensuring it recognizes the new sensor.
FAQ
What’s the difference between programming and resetting TPMS?
Programming a TPMS sensor is the process of syncing a new tire pressure sensor to the vehicles computer systems. Resetting a TPMS system is the process of recalibrating the existing tire pressure sensors current air pressures to the vehicles computer system as a new air pressure reference value.
How long do tire sensors typically last?
Tire pressure sensors generally have a lifespan of 5 to 10 years or about 100,000 miles, though this can vary based on driving conditions, frequency of use, and maintenance.
Can I Drive Even when a TPMS Sensor is Bad?
While it’s possible to drive with a faulty sensor, it’s not advisable as it compromises the TPMS’s ability to monitor tire pressure accurately.
How Much Does it Cost to Replace a TPMS Sensor?
The cost can vary widely depending on the vehicle and tire shop, but it typically ranges from $50 to $250 per sensor, including parts and labor.
Can Tire Sensors Affect Vehicle Alignment?
Directly, no. However, incorrect tire pressure readings can lead to uneven tire wear, which may eventually impact alignment.
Are Aftermarket Tire Sensors Reliable?
Many aftermarket sensors offer comparable quality to OEM parts. Use aftermarket sensors that are universal (they can operate on 315 MHz or 433 MHz frequencies).
About the Author
STEFAN A.
Professional Automotive Technician – I am currently an automotive technician in New Jersey and have worked in private shops as well as dealerships. When I am not writing articles I am wrenching on race cars and driving radio controlled cars at the track!
Please note that this blog post contains Amazon affiliate links. This means that if you make a purchase through one of these links, we at TPMSRESET.COM may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products that we personally use and believe in. Thank you for supporting us.